Symmetri has joined Yes&.
We have some exciting news. Symmetri has decided to join the Yes& team to discover more possibilities to our clients.

We have some exciting news. Symmetri has decided to join the Yes& team to discover more possibilities to our clients.

 Posted by Carl Triemstra on December 9, 2014
Posted by Carl Triemstra on December 9, 2014
Nothing is worse than having your website black flagged or blocked by Google. Businesses of all sizes rely on Google search traffic to acquire new leads, offer products and services, and generate sales or donations.hLet’s consider the statistics-- almost 64% of internet search traffic is fueled by organic search and current search rankings give Google a market share of close to 68% (upwards of 80% for mobile search). This is effectively a search monopoly. Follow these 10 steps to ensure your website is not reported as "hacked" in Google search results.
In order for your business to have a chance online, it must be in good standing with Google. New websites that appear online are indexed almost automatically by Googlebots. It is possible to manually revoke access to your site for indexing by these bots. To ensure that the Googlebot is not blocked by your website:
Once you have cleared through this basic setup, your site will be indexed by Google and begin to rank within search results pages. These steps will put you in a good position to deal with any future flagging or blocking by Google due to a suspected compromise. If Google detects that your site could be compromised and potentially dangerous, they will begin to warn potential visitors in the search results.

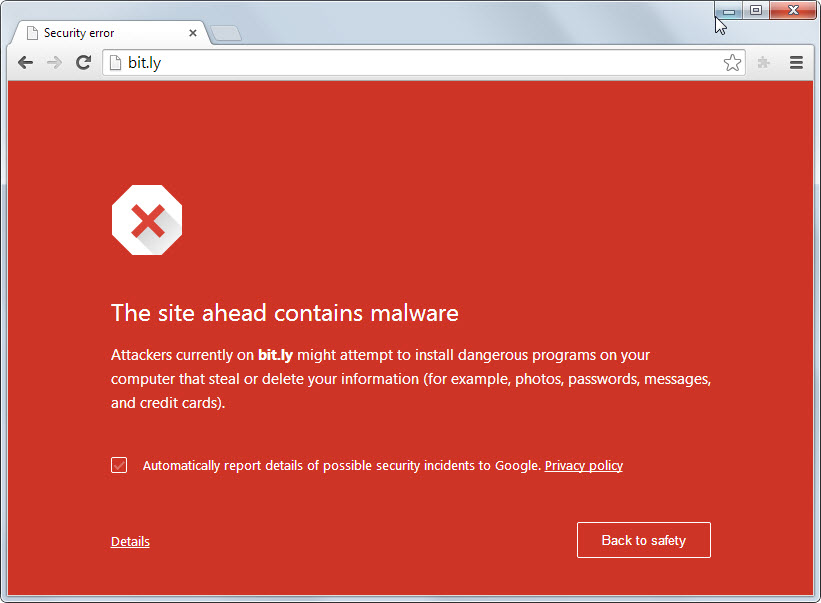
The phrase “This site may be hacked.” will begin to appear directly underneath your search results. Needless to say, this will not encourage a higher click through rate and will have a significant negative impact on your site traffic. Other phrases may report as the following.
Google presents the following explanation and rationale for why these messages may appear under your site within search results.
To protect the safety of our users, we show this warning message for search results that we believe may have been hacked or otherwise compromised. If a site has been hacked, it typically means that a third party has taken control of the site without the owner’s permission. Hackers may change the content of a page, add new links on a page, or add new pages to the site. The intent can include phishing (tricking users into sharing personal and credit card information) or spamming (violating search engine quality guidelines to rank pages more highly than they should rank).
In some situations your website or server may be compromised by a Malware infection that could affect other computers. Modern web browsers like Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox check against these flags and trigger a warning message in the browser environment, effectively putting a halt to web traffic.
Run the Google Safe Browsing Diagnostic.
https://www.google.com/safebrowsing/diagnostic?site=Google.com
The "?site=" url parameter will allow you to run any site you want through the Safe Browsing Diagnostic. Swap out the Google.com at the end of this address with your website and run the diagnostics. This diagnostic page will give you an extremely valuable at-a-glance summary page of the status of your site over the last 90 days. Use this information to guide the rest of your investigation and cleaning efforts.
Google may or may not provide additional information to you as a site owner. It will be on you to investigate the issue and determine how your site has been compromised. Depending on the level of the compromise, this may require a complete server restore from a known clean backup. This could take your entire website offline for hours or days depending on your ability to respond to such an emergency situation. Google outlines a procedure for quarantining your site, discovering the issue, fixing the problem, and resubmitting to Google for a clean bill of health.
The aforementioned scenario puts you into a reactive posture as a webmaster or site owner. If you are a marketing manager getting ready to launch a new campaign designed to increase traffic to your site, this will put a big monkey wrench in the works. A better approach is to proactively monitor and protect your site from vulnerabilities.
Maintaining the security of your hosting environment is an important step. Depending on your hosting support contract, this may or may not be addressed in a timely manner by your web hosting provider. Contact your hosting provider and find out what their policy is for securing your hosting environment against known vulnerabilities.
Once you have taken care of the general security of your web hosting environment, you need to address each of your websites. Static HTML websites that are only accessible for edits via FTP are usually quite safe from attacks. Code scripts like content management systems that allow for user logins and file uploads create possible security compromises by their very nature. If you are the owner of an open source CMS like Drupal, then you have additional concerns as security releases are announced.
SA-CORE-2014-005 was released on October 15th of 2014. This vulnerability was actively sought out by hackers from around the world and exploited by black-hat scripters.
Update: Multiple exploits have been reported in the wild following the release of this security advisory, and Drupal 7 sites which did not update soon after the advisory was released may be compromised. See this follow-up announcement for more information:https://www.drupal.org/PSA-2014-003
If you own a Drupal 7 website and you are not sure about the level of your updates, it is recommended that you check immediately to ensure your site is at 7.32 or later. In some instances, Google may report a warning on search results based solely on an algorithmic check of your website’s Drupal version. In this case, your website does not even need to be compromised by a hacker in order to trigger the warning message. Using a tool like Drupal X Ray can help to expose vulnerabilities by checking the update level of your Drupal website, but it is only the first step.
At Commercial Progression we take a PRO-ACTIVE stance to Drupal web monitoring and maintenance. All of our DrupalCare clients are routinely reviewed for known vulnerabilities. Updating your website before there is a problem is key to the health of your web presence.
Our 10 step Drupal security audit guide demonstrates a core part of our regular client review process. Download this guide for a step by step process to secure your Drupal website today.